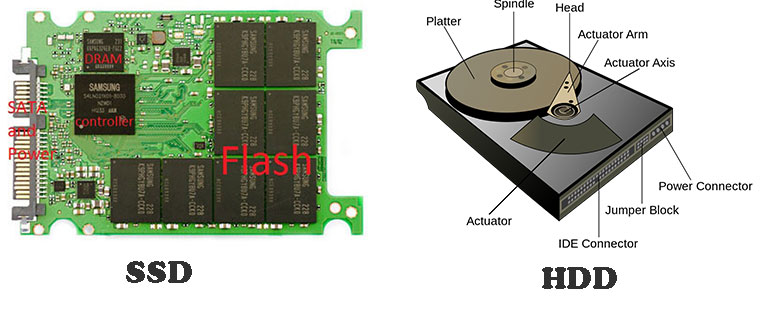
How does a SATA-SSD improve computer's performance?
The performance of your computer might be significantly enhanced by switching to a SATA SSD. Games and other applications will load more quickly, apps will start more quickly, and boot times will be shorter. This is because, in comparison to conventional hard drives, SSDs have significantly lower latency and faster read/write speeds. SSDs are more reliable since they don't have any moving parts, which also makes them more resistant to physical shocks. All things considered, utilizing a SATA SSD makes your everyday computer chores faster and more responsive.
When should consider upgrading to a SATA-SSD?
If your system is slow, especially when booting up, launching apps, or transferring files, you should think about upgrading to a SATA SSD. An SSD can significantly improve your workflow if you discover that your hard drive is operating at a high speed all the time. Additionally, an SSD is a better option if you need a portable device with more durability and dependability because it has less moving parts, making it less vulnerable to harm from drops or movement.
Is a SATA-SSD compatible with any computers?
The majority of contemporary PCs with a SATA connector can use SATA SSDs. Since SATA ports are supported by nearly all desktops and laptops made in the past ten years, replacing an old HDD with an SSD is simple. To guarantee compatibility, it's best to review the manufacturer's documentation or the specs of your machine. Rarely, especially with very old machines, you might require extra hardware or an adapter to finish the installation.
What are the benefits of using a SATA-SSD in a server computer?
Faster data access speeds, lower latency, and enhanced overall performance are just a few advantages of using a SATA SSD in a server. These benefits are essential for applications like virtual machines and databases that need to perform read/write operations quickly. In addition, SSDs produce less heat and use less power than conventional hard drives, which can result in reduced operating expenses and increased dependability. Servers can more effectively manage growing workloads by switching to SATA SSDs.
Would a SATA-SSD be suitable for gaming?
Compared to conventional hard drives, a SATA SSD provides faster load times, smoother gameplay, and faster level transitions, making it an excellent choice for gamers. Performance will be enhanced and lag will be decreased when games put on an SSD start up and in-game assets load more rapidly. Even though SATA SSDs may not be as fast as NVMe SSDs, they are still a significant upgrade over HDDs and are frequently more affordable for gamers who want to improve their setup.
What is the difference between a SATA-SSD & an NVMe-SSD?
A SATA SSD and an NVMe SSD differ primarily in their performance and interfaces. Because SATA SSDs utilize the outdated SATA interface, their top speeds are just about 600 MB/s. Conversely, NVMe SSDs, which employ the PCIe interface, offer noticeably faster speeds—often surpassing 3,000 MB/s. NVMe SSDs are perfect for high-demand applications because they provide improved overall performance, reduced latency, and faster data transfer rates. SATA SSDs, on the other hand, are typically less expensive while still offering a significant performance improvement over conventional HDDs.
Could a SATA-SSD improve programming workflow?
Yes, you can greatly enhance your programming workflow using a SATA SSD. Your development environment, code repositories, and project files load faster when you have faster data access speeds, which boosts productivity all around. A more effective and responsive development process is made possible by the acceleration of tasks including code compilation, test execution, and version control system management. An SSD offers a discernible gain over a conventional hard disk, regardless of whether you're working on big tasks or juggling several apps at once.
Can use a SATA-SSD in an external enclosure?
A SATA SSD can be used in an external container, yes. With this configuration, you may use the SSD as an external storage device and enjoy the advantages of solid-state storage, like increased durability and quicker data transfer rates. External enclosures are portable and adaptable because they usually connect to your PC via USB. This is a fantastic choice if you want to increase the amount of storage you have or use the SSD to move big files across devices.
What size of SATA-SSD should get for computer?
Your unique requirements and usage habits will determine the size of the SATA SSD you should purchase. A 500GB to 1TB SSD provides a decent trade-off between price and storage capacity for the majority of users. This gives room for media and personal projects in addition to the operating system, apps, and other data. However, a greater capacity SSD might be useful if you work with enormous files, including massive databases or high-resolution films. To choose the ideal size for your setup, consider your present storage needs as well as your future requirements.
Can use a SATA-SSD as a boot drive?
Indeed, one of the best computer upgrades you can make is to use a SATA SSD as the boot disk. An SSD's quick read speeds significantly shorten boot times, allowing your operating system to launch in a matter of seconds. Additionally, faster loading times for applications and system functions enhance responsiveness overall. Installing your operating system on your SSD is the first step in setting it up as the boot drive; this may include a fresh installation or a system clone.
Does a SATA-SSD affect gaming performance?
By providing faster transitions, cutting down on stutters during gameplay, and decreasing loading times, a SATA SSD can greatly improve gaming performance. Faster data retrieval is advantageous for games running on an SSD, especially when loading new levels or assets. A SATA SSD makes sure that data-intensive tasks are carried out quickly and smoothly, which improves the overall gaming experience even though it might not directly raise frame rates.
What factors should consider when choosing a SATA-SSD?
Think about things like pricing, endurance, performance, and capacity while selecting a SATA SSD. Your storage demands will determine the capacity; larger drives have more space but are more expensive. Performance is enhanced with higher-end SSDs; speed varies by device. The amount of data that the SSD can write over its lifetime is indicated by endurance, which is expressed in TBW (terabytes written). Finally, think about your budget; strike a cost-performance balance that meets your needs.
Would a SATA-SSD be good for storing my large databases?
Large databases can be efficiently stored on a SATA SSD, especially if your applications require low latency and fast read/write speeds. By accelerating the construction of indexes, backup procedures, and query execution, SSDs enhance database performance. A SATA SSD offers a more affordable option with notable enhancements over conventional hard drives, even though NVMe SSDs provide even better performance. When choosing the right storage solution, take into account your unique database workload and access patterns.
Are there different form factors for SATA-SSDs?
Indeed, SATA SSDs are available in a variety of form sizes to accommodate a range of devices. The most common form factors are mSATA and M.2, which are frequently found in ultrabooks, tablets, and small PCs, and the 2.5-inch drive, which is frequently seen in desktops and laptops. Although the SATA interface is used by all of these form factors, their actual dimensions and ports vary. Make sure the form factor you select fits the slots or storage bays on your device.
Would a SATA-SSD improve software development tasks?
Through faster file access, shorter compile times, and improved system responsiveness, using a SATA SSD can significantly improve software development activities. An SSD increases the efficiency of tasks like managing sizable code repositories, loading integrated development environments (IDEs), and executing automated tests. Developers may concentrate more on coding and less on waiting for procedures to finish thanks to SSDs' fast data access, which keeps workflows efficient.