What is Combined RAID - Nested RAID / Hybrid RAID?
RAID 01 is a data storage arrangement that offers increased storage capacity and data redundancy by combining the capabilities of RAID 0 array (striping) with RAID 1 array (mirroring). In RAID 01, data is spread across multiple drives, and a duplicate copy is made on a different set of disks. Even in the event that one drive fails, this configuration ensures that the data may be retrieved from the mirrored drive. Performance and resilience are combined in this setup.
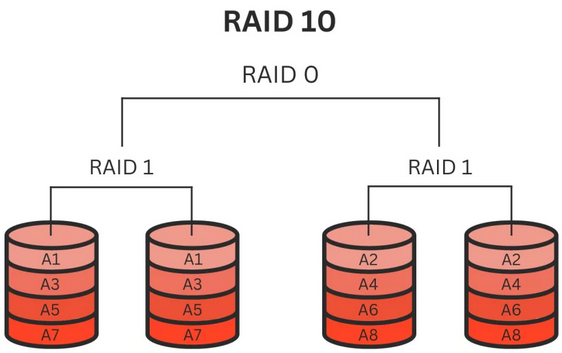
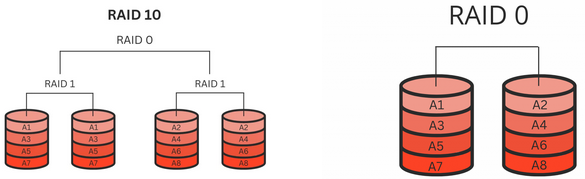
To improve efficiency and guarantee data redundancy, RAID 10 is a kind of nested RAID level that combines the features of RAID 0 (striping) and RAID 1 (mirroring). For higher read and write rates, RAID 10 divides data into stripes and duplicates it over many drive sets. Applications needing high performance and data protection levels will find this configuration ideal since it combines the performance advantages of striping with the redundancy of mirroring.
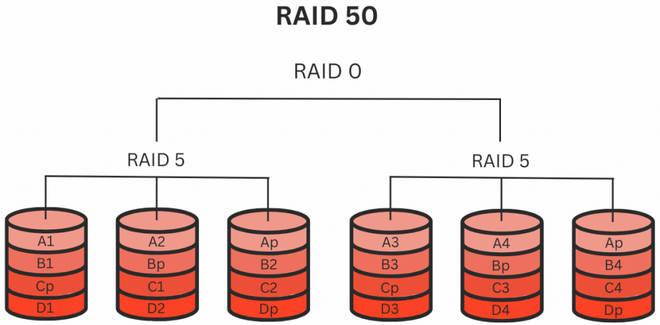
RAID 50 is a hybrid RAID level that balances fault tolerance and performance by combining the characteristics of RAID 0 (striping) and RAID 5 (parity-based striping). Data is striped across several sets of disks in RAID 50, each of which is striped for improved performance and parity information for fault tolerance. The advantages of parity-based striping for fault tolerance and striping for performance are both provided by this setup.
RAID 5 + 1
In order to improve performance and redundancy, RAID 51 is a hybrid RAID configuration that combines the characteristics of RAID 5 and RAID 1. Multiple disk sets are utilized in RAID 51, each of which is set up in a parity-based striping (RAID 5) configuration before being replicated using RAID 1 (mirroring). With more redundancy and better speed, this setup combines the advantages of RAID 5 and RAID 1.
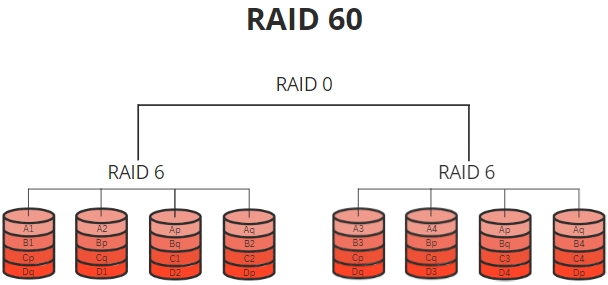
In order to improve performance and fault tolerance, RAID 60 is a RAID level that combines the characteristics of RAID 0 (striping) and RAID 6 (dual parity). Data is striped across several sets of drives with dual parity for fault tolerance in a RAID 60 configuration. Those sets are then striped for improved performance. Applications needing high performance and data security levels can use this configuration since it combines the advantages of RAID 0 for throughput with RAID 6 for fault tolerance.
High performance and fault tolerance are provided by RAID 100, a RAID level that combines the capabilities of RAID 0 (striping) and RAID 10 (mirroring and striping). Different sets of disks are utilized in RAID 100, each of which is configured in RAID 10 before being striped using RAID 0. High performance and data protection levels are offered by this configuration, which combines the advantages of RAID 0 and RAID 10.